Main MULTIDIP routines. More...
Data Types | |
| type | IntermediateState |
| Intermediate state. More... | |
Functions/Subroutines | |
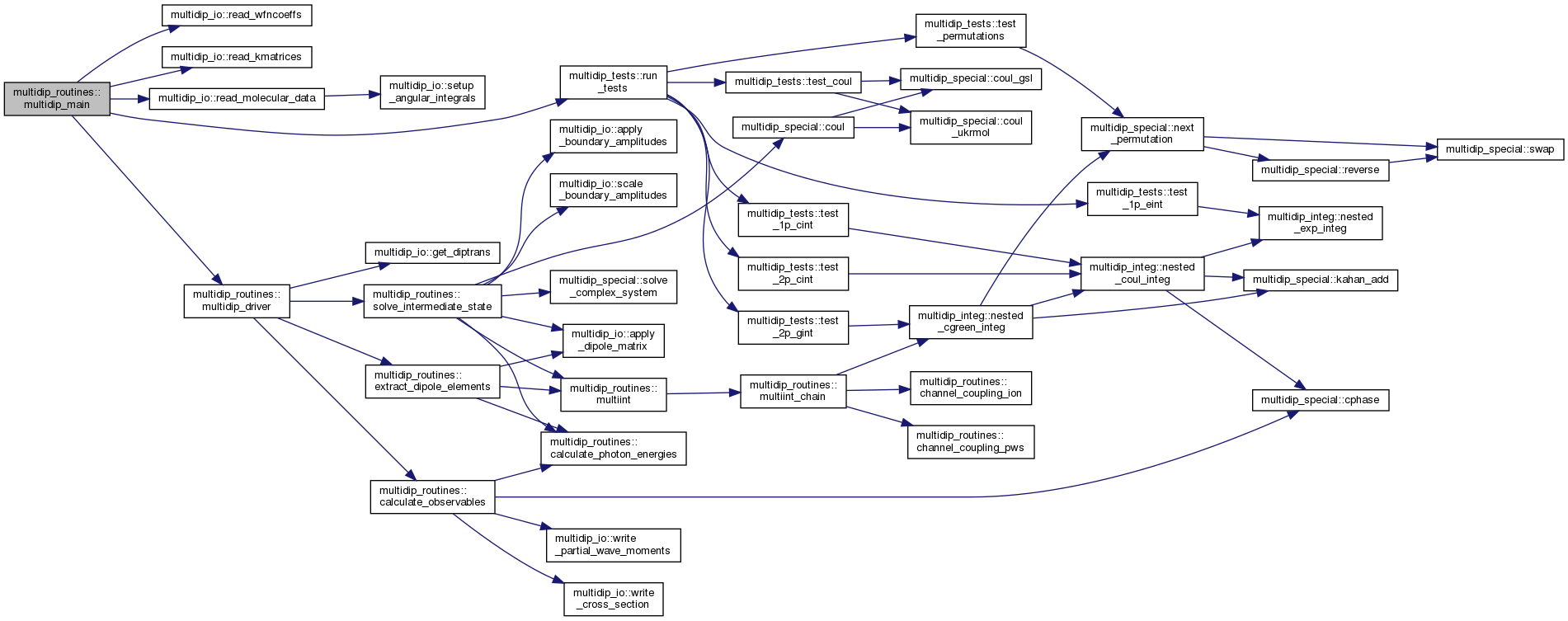
| subroutine | multidip_main |
| MULTIDIP main subroutine. More... | |
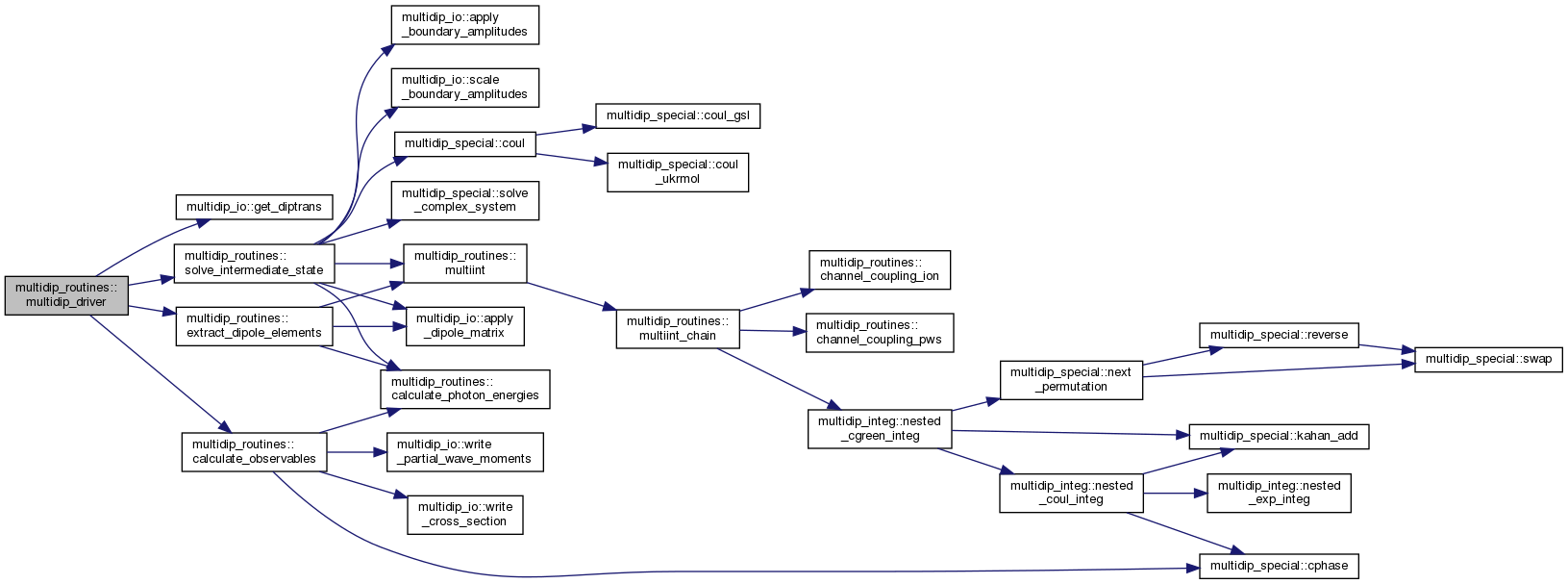
| subroutine | multidip_driver (order, moldat, km, ak, omega, polar, verbose) |
| Central computation routine. More... | |
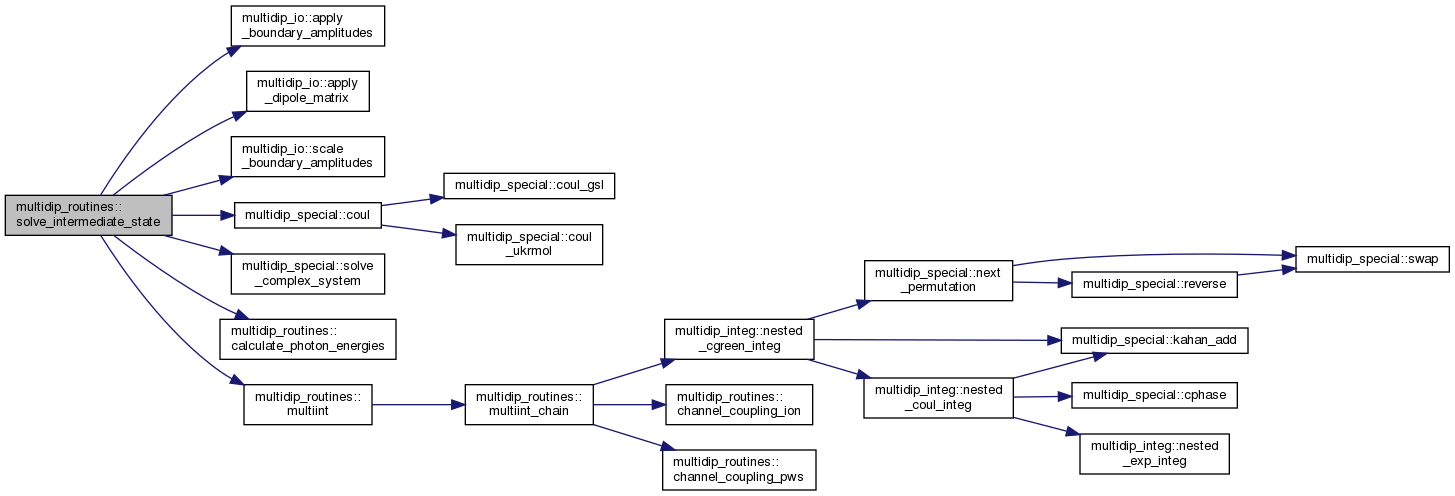
| subroutine | solve_intermediate_state (moldat, order, Ephoton, irri, icomp, s, mgvnn, mgvn1, mgvn2, km, state, verbose) |
| Calculate intermediate photoionisation state. More... | |
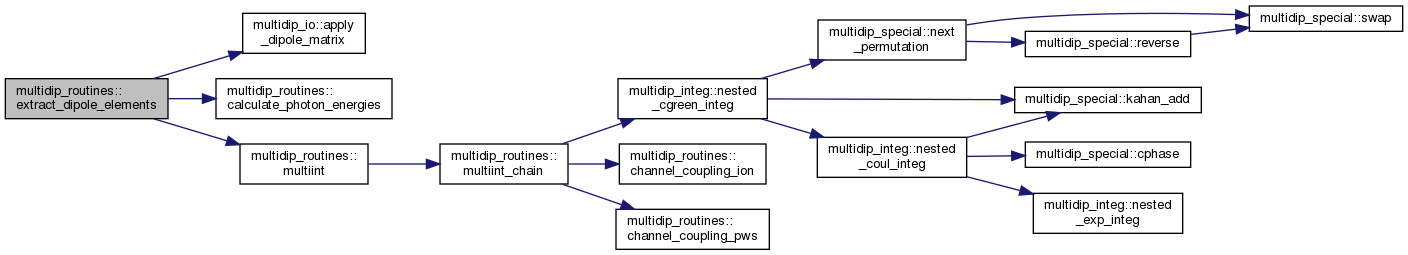
| subroutine | extract_dipole_elements (moldat, order, Ephoton, irri, icomp, s, mgvnn, mgvn1, mgvn2, km, ak, state, verbose) |
| Calculate dipole elements from intermediate and final states. More... | |
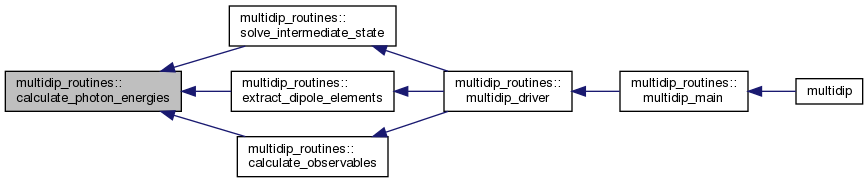
| subroutine | calculate_photon_energies (IP, Ephoton, omega) |
| Calculate energy of each photon. More... | |
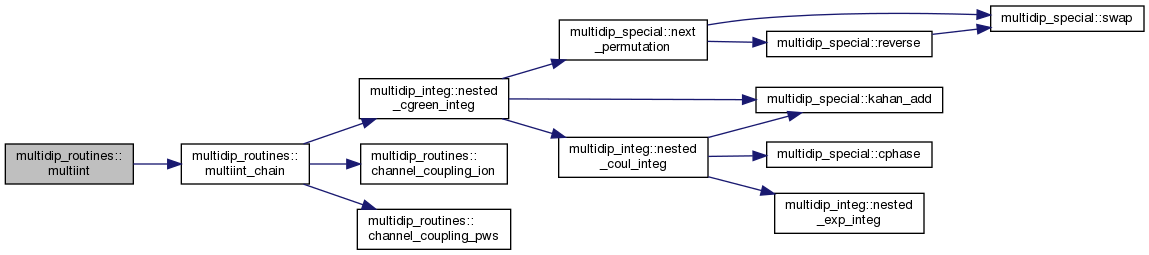
| subroutine | multiint (moldat, Ei, omega, ie, state, sb, dip) |
| Evaluate the correction dipole integral for all orders. More... | |
| recursive complex(wp) function | multiint_chain (moldat, Ei, omega, ie, c, N, state, ichanf, sb, k, l, m) |
| Calculate dipole correction integrals at given absorption depth. More... | |
| real(wp) function | channel_coupling_ion (moldat, dcomp, mgvnf, mgvni, ichanf, ichani) |
| Ion channel dipole coupling. More... | |
| real(wp) function | channel_coupling_pws (moldat, dcomp, mgvnf, mgvni, ichanf, ichani) |
| Partial wave channel dipole coupling. More... | |
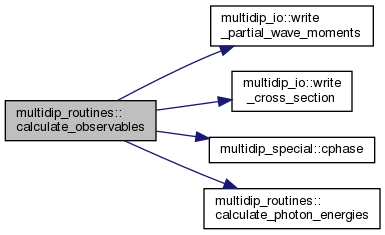
| subroutine | calculate_observables (moldat, order, state, escat, Ei, Ephoton, polar) |
| Calculate partial wave dipoles, oriented dipoles and cross sections. More... | |
Detailed Description
Main MULTIDIP routines.
- Date
- 2020
Function/Subroutine Documentation
◆ calculate_observables()
| subroutine multidip_routines::calculate_observables | ( | type(moleculardata), intent(in) | moldat, |
| integer, intent(in) | order, | ||
| type(intermediatestate), intent(in), pointer | state, | ||
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(in) | escat, | ||
| real(wp), intent(in) | Ei, | ||
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(in) | Ephoton, | ||
| complex(wp), dimension(:, :), intent(in) | polar | ||
| ) |
Calculate partial wave dipoles, oriented dipoles and cross sections.
- Date
- 2020
Given the uncontracted partial wave dipoles
\[ M_{i_f, l_f, m_f, j_1, \dots, j_n}^{(n)} \]
calculated in extract_dipole_elements, where \( i_f \) is the index of the final ion state, \( l_f \) and \( m_f \) denote the emission partial wave and \( j_1, \dots, j_n \) are the indices of components of the polarisation vectors, evaluate the partial wave transition matrix elements
\[ M_{i_f, l_f, m_f} = \mathrm{i}^{-l_f} \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{i} \sigma_f} \sum_{j_1, \dots, j_n} \epsilon_{j_1} \dots \epsilon_{j_n} M_{i_f, l_f, mf_, j_1, \dots, j_n}^{(n)} \]
contracted with the polarisation vectors themselves, and the emission-direction- and polarisation-direction-averaged generalized cross section
\[ \sigma_f^{(n)} = 2\pi (2\pi\alpha\omega/3)^n \sum_{j_1, \dots, j_n} \left| M_{i_f, l_f, m_f, j_1, \dots, j_n} \right|^2 \]
The factor 1/3 is only present once for each photon with zero polarisation (averaged).
- Parameters
-
[in] moldat MolecularData object with data read from the file molecular_data. [in] order Perturbation order matrix elements (= number of absorbed photons). [in] state Tree of intermediate and final states. [in] escat Scattering energies in a.u., as stored in the K-matrix files. [in] Ei Total energy of the initial state. [in] Ephoton Fixed photon energies in a.u. or zeros for flexible photons. [in] polar Photon polarisations or zeros for polarisation averaging.
Definition at line 990 of file multidip_routines.F90.

◆ calculate_photon_energies()
| subroutine multidip_routines::calculate_photon_energies | ( | real(wp), intent(in) | IP, |
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(in) | Ephoton, | ||
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(inout), allocatable | omega | ||
| ) |
Calculate energy of each photon.
- Date
Calculate energies of all photons. The positive elements of the input array Ephoton specify fixed energies of selected photons. The remaining energy needed to reach the ionisation potential is divided among the remaining photons.
- Parameters
-
[in] IP Summed energy of all photons. [in] Ephoton User-specified fixed energies of photons or zeros for flexible photons. [in,out] omega Calculated energies of all photons.
Definition at line 704 of file multidip_routines.F90.
◆ channel_coupling_ion()
| real(wp) function multidip_routines::channel_coupling_ion | ( | type(moleculardata), intent(in) | moldat, |
| integer, intent(in) | dcomp, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvnf, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvni, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | ichanf, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | ichani | ||
| ) |
Ion channel dipole coupling.
- Date
- 2020
Returns the ion transition dipole element between the channels. This is diagonal in quantum numbers of the partial waves and simply equal to the corresponding N-electron propery integral.
- Parameters
-
[in] moldat MolecularData object with data read from molecular_data. [in] dcomp Index of the Cartesian component of the dipole operator. [in] mgvnf MGVN of the final state channel. [in] mgvni MGVN of the initial state channel. [in] ichanf Index of the final state channel. [in] ichani Index of the initial state channel.
Definition at line 894 of file multidip_routines.F90.

◆ channel_coupling_pws()
| real(wp) function multidip_routines::channel_coupling_pws | ( | type(moleculardata), intent(in) | moldat, |
| integer, intent(in) | dcomp, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvnf, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvni, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | ichanf, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | ichani | ||
| ) |
Partial wave channel dipole coupling.
- Date
- 2020
Returns the partial wave transition dipole element between the channels. This is diagonal in the ion states and proportional to the Gaunt coefficient.
- Parameters
-
[in] moldat MolecularData object with data read from molecular_data. [in] dcomp Index of the Cartesian component of the dipole operator. [in] mgvnf MGVN of the final state channel. [in] mgvni MGVN of the initial state channel. [in] ichanf Index of the final state channel. [in] ichani Index of the initial state channel.
Definition at line 933 of file multidip_routines.F90.

◆ extract_dipole_elements()
| subroutine multidip_routines::extract_dipole_elements | ( | type(moleculardata), intent(in) | moldat, |
| integer, intent(in) | order, | ||
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(in) | Ephoton, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | irri, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | icomp, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | s, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvnn, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvn1, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvn2, | ||
| type(kmatrix), dimension(:), intent(in), allocatable | km, | ||
| type(scatakcoeffs), dimension(:), intent(in), allocatable | ak, | ||
| type(intermediatestate), intent(inout), pointer | state, | ||
| logical, intent(in) | verbose | ||
| ) |
Calculate dipole elements from intermediate and final states.
- Date
- 2020
Calculates the transition dipole matrix element between the last intermediate state and the final stationary photoionization state.
- Parameters
-
[in] moldat MolecularData object with data read from the file molecular_data. [in] order Perturbation order of the intermediate state to calculate. [in] Ephoton Fixed photon energies in a.u. or zeros for flexible photons. [in] irri Index of the previous (parent) state irreducible representation among those present in molecular_data. [in] icomp Which Cartesian component of the dipole operator will give rise to the intermediate state. [in] s Which "transition" in molecular_data corresponds to the action of this dipole component on parent. [in] mgvnn MGVN of the previous intermediate state. [in] mgvn1 Ket MGVN for the transition "s" as stored in molecular_data. [in] mgvn2 Bra MGVN for the transition "s" as stored in molecular_data. [in] km KMatrix objects for relevant irreducible representations with data read from RSOLVE K-matrix files. [in] ak Wave function coeffs (from RSOLVE) for the same set of irrs as km. [in,out] state Tree of intermediate states, pointing at the previous intermediate state to develop into next state. [in] verbose Debugging output intensity.
Definition at line 544 of file multidip_routines.F90.

◆ multidip_driver()
| subroutine multidip_routines::multidip_driver | ( | integer, intent(in) | order, |
| type(moleculardata), intent(in) | moldat, | ||
| type(kmatrix), dimension(:), intent(in), allocatable | km, | ||
| type(scatakcoeffs), dimension(:), intent(in), allocatable | ak, | ||
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(in) | omega, | ||
| complex(wp), dimension(:, :), intent(in) | polar, | ||
| logical, intent(in) | verbose | ||
| ) |
Central computation routine.
- Date
- 2020
This subroutine drives the calculation. First it obtains all intermediate states, then it calculates the final photoionization state, and evaluates the dipole elements and generalized cross sections. The core of the work is the evaluation of all matrix elements of the type
\[ M_{fi,k_n,\dots,k_i} = \langle \Psi_{f}^{(-)} | x_{k_n} \dots \hat{G}^{(+)} x_{k_2} \hat{G}^{(+)} x_{k_1} | \Psi_i \rangle \]
where \( x_j \) is the j-th component of the dipole operator, followed by reduction of this tensor with all provided photon field polarisations \( \epsilon_j \):
\[ M_{fi} = \sum_{k_n,\dots,k_1} \epsilon_{k_n} \dots \epsilon_{k_1} M_{fi,k_n,\dots,k_1} \]
The sequence \( k_1, k_2, \dots \) is referred to as component "history" or "chain" in the code.
- Parameters
-
[in] order Order of the process (= total number of absorbed photons). [in] moldat MolecularData object with data read from the file molecular_data. [in] km KMatrix objects for relevant irreducible representations with data read from RSOLVE K-matrix files. [in] ak Wave function coeffs (from RSOLVE) for the same set of irrs as km. [in] omega Fixed photon energies in a.u. or zeros for flexible photons. [in] polar Photon polarisation vectors or zeros for polarisation averaging. [in] verbose Debugging output intensity.
Definition at line 223 of file multidip_routines.F90.

◆ multidip_main()
| subroutine multidip_routines::multidip_main | ( | ) |
MULTIDIP main subroutine.
- Date
- 2020
Read the input namelist &mdip from the standard input, call routines for reading the input file, and then call the main computational routine. Alternatively, when the "--test" switch is present on the command line, it will run a few unit tests.
Definition at line 94 of file multidip_routines.F90.
◆ multiint()
| subroutine multidip_routines::multiint | ( | type(moleculardata), intent(in) | moldat, |
| real(wp), intent(in) | Ei, | ||
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(inout), allocatable | omega, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | ie, | ||
| type(intermediatestate), intent(in), pointer | state, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | sb, | ||
| complex(wp), dimension(:), intent(inout), allocatable | dip | ||
| ) |
Evaluate the correction dipole integral for all orders.
- Date
- 2020
If the parent intermediate state has a non-vanishing outer region part, integrate the final wave function with it and multiply by the associated expansion coefficients 'ap'. Then, iteratively, for all parent states of the parent state, add their contribution by means of the Coulomb-Green's function (multiplied by their expansion coefficients). The deeper in the absorption chain we get, the more dimensions the resulting Coulomb-Green's integral has.
- Parameters
-
[in] moldat MolecularData object with data read from molecular_data. [in] Ei Total energy of the initial state. [in] omega Energy of all photons. [in] ie Local energy index. [in] state Tree of parent intermediate states pointed to the last intermediate state. [in] sb Kind (sign) of the outer-most Coulomb-Hankel function. [out] dip Evaluated multi-photon matrix element.
Definition at line 735 of file multidip_routines.F90.
◆ multiint_chain()
| recursive complex(wp) function multidip_routines::multiint_chain | ( | type(moleculardata), intent(in) | moldat, |
| real(wp), intent(in) | Ei, | ||
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(inout), allocatable | omega, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | ie, | ||
| real(wp) | c, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | N, | ||
| type(intermediatestate), intent(in), pointer | state, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | ichanf, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | sb, | ||
| complex(wp), dimension(:), intent(inout), allocatable | k, | ||
| integer, dimension(:), intent(inout), allocatable | l, | ||
| integer, dimension(:), intent(inout), allocatable | m | ||
| ) |
Calculate dipole correction integrals at given absorption depth.
- Date
- 2020
Recursively evaluates the outer region contributions multi-photon transition element contributions from all combinations of channels at all absorption levels that share the initial sequence given by k, l and m.
- Parameters
-
[in] moldat MolecularData object with data read from molecular_data. [in] Ei Total energy of the initial state. [in] omega Energy of all photons. [in] ie Local energy index. [in] c Dipole exponential damping coefficient. [in] N Index of the dipole operator to consider on this recursion level. [in] state Tree of parent intermediate states pointed to the last intermediate state. [in] ichanf Final channel after action of the dipole operator at this recursion level. [in] sb Kind (sign) of the outer-most Coulomb-Hankel function. [in,out] k Linear momenta of the final and initial dipole transition channels for at previous recursion levels. [in,out] l Angular momenta of the final and initial dipole transition channels for at previous recursion levels. [in,out] m Angular projections of the final and initial dipole transition channels for at previous recursion levels.
- Returns
- integ Evaluated multi-photon matrix element.
Definition at line 806 of file multidip_routines.F90.
◆ solve_intermediate_state()
| subroutine multidip_routines::solve_intermediate_state | ( | type(moleculardata), intent(in) | moldat, |
| integer, intent(in) | order, | ||
| real(wp), dimension(:), intent(in) | Ephoton, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | irri, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | icomp, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | s, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvnn, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvn1, | ||
| integer, intent(in) | mgvn2, | ||
| type(kmatrix), dimension(:), intent(in), allocatable | km, | ||
| type(intermediatestate), intent(inout), pointer | state, | ||
| logical, intent(in) | verbose | ||
| ) |
Calculate intermediate photoionisation state.
- Date
- 2020
Solve the intermediate state equation
\[ (E_i + j \omega - \hat{H}) \Psi_j = \hat{D} \Psi_{j-1} \]
with the right-hand side based on the state provided as argument 'state'.
- Parameters
-
[in] moldat MolecularData object with data read from the file molecular_data. [in] order Perturbation order of the intermediate state to calculate. [in] Ephoton Fixed photon energies in a.u. or zeros for flexible photons. [in] irri Index of the previous (parent) state irreducible representation among those present in molecular_data. [in] icomp Which Cartesian component of the dipole operator will give rise to the intermediate state. [in] s Which "transition" in molecular_data corresponds to the action of this dipole component on parent. [in] mgvnn MGVN of the previous intermediate state. [in] mgvn1 Ket MGVN for the transition "s" as stored in molecular_data. [in] mgvn2 Bra MGVN for the transition "s" as stored in molecular_data. [in] km KMatrix objects for relevant irreducible representations with data read from RSOLVE K-matrix files. [in,out] state Tree of intermediate states, pointing at the previous intermediate state to develop into next state. [in] verbose Debugging output intensity.
Definition at line 352 of file multidip_routines.F90.